An emerging market is a nation that is becoming more engaged with global markets as it grows and develops.
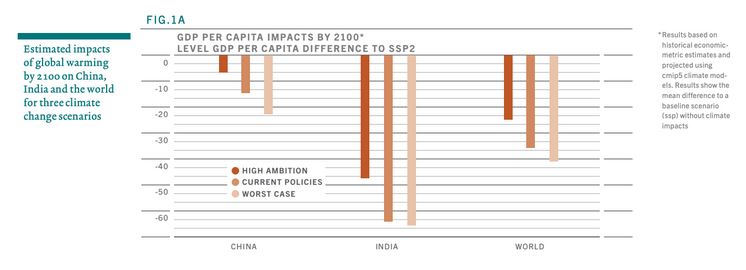
Emerging markets have huge investment potential with yearly GDP growth that triples that of the average developed nation. However, this growth and development also brings the threat of climate disasters as GHG emissions are expected to rise. Without adequate capital and infrastructure, developing countries disproportionately feel the effects of climate change.
While the opportunity for investment is legitimate in emerging markets, responsible investment is crucial.
Why is Climate Change an important issue for Emerging Markets?
- Emerging countries are at risk of suffering disproportionately from the effects of global warming
- Emerging markets are more susceptible to rising sea levels, droughts, and slumps in agricultural production
- Population growth combined with increased development results in a major need for more electricity and energy
- With increased development, these emerging economies have the greatest opportunity to implement clean energy sources
India
Green Bonds in India
- India has the second largest market for green bonds – $10.3 Billion in 2019.
- Private issuance allows Indian companies to raise capital at a fixed rate rather than the floating rate of a loan.
- Ghaziabad Municipal Corporation – first municipal corporation to issue green bond in domestic market
- Will construct a tertiary sewage treatment plant with a coupon of 8.1% on a 10-year note.
- JSW Hydro Energy Ltd – first hydro issues raised $707 Million in overseas market offering a coupon of 4.125$ per year, payable semi-annually.
- Shriram Transport Finance – Raised $500 million at a coupon rate of 4.4 via social bonds; conducts ESG research and corporate governance research.
- UltraTech Cement Ltd – $400 million sustainability linked bond – aims to reduce 22.2 percent of carbon emissions for every ton of cement material it produces by 2030
- Ghaziabad Municipal Corporation – first municipal corporation to issue green bond in domestic market
- Private issuance allows Indian companies to raise capital at a fixed rate rather than the floating rate of a loan.
Projects
- Clean Technology Fund (CTF)
- Administered by the World Bank to finance clean technology projects.
- $775 million investment plan to support the development of over 3GW of new Solar power.
- Working to offset high upfront costs of large-scale solar park projects and to de-risk investments in rooftop solar photovoltaics to unleash full market potential.
- Areas of focus:
- Development policy loan on environmental sustainability and climate change.
- National mission for enhanced energy efficiency.
- Partial risk guarantee for energy efficiency tech.
- Support for Jawaharlal Nehru National Solar Mission
- Rajasthan Renewable Energy Transmission Investment Program
- CIF funding – $200 Million USD
- Blended finance with State of Rajasthan and ADB Bank CTF Financing
- $800 million USD
- CTF is responsible for most of the infrastructure and linking of the project but private sectors will support PV array and generation facilities.
- Higher than estimated reduction of GHG
- Solar Rooftop Investment Program Guaranteed by India
- CIF funding – $175 Million USD
- World Bank – $625 Million USD
- Concessional debt financing for setting up rooftop solar panels.
- Will allow access to about $1 Billion USD in funding
- Grid-Connected Rooftop Solar Program
- CIF Funding – $125 Million USD
- 1911 MW of rooftop solar
- Saving 1.7 million tonnes of CO2 emissions
- Creating 50,000 jobs
Government Policies
Policies to Increase Investment:
| Policy Type: | Description: |
| Subsidies | In 2017, the Indian government gave $0.8 billion USD in subsidies for clean energy projects. However, while the subsidies for coal and fossil fuel projects are decreasing, they still are three times larger than clean energy. Ex: Subsidies for diesel generators, 25% of the cost of a generator set. |
| Technology and Quality Upgradation Support Subsidy | Main goal: Promote use of energy efficient technologies and manufacturing processes so as to reduce cost of production and emissions of GHGs – Government will provide 25% of project cost for the implementation of energy efficient technologies |
| Integrated Development of Leather Sector | Subsidy requires state government / state pollution control checks that production of leather is environmentally sound with waste water management. |
| Solar Energy Scheme for Power Looms | – Subsidies use of solar panels for power looms – Depends on size of panels and amount of energy |
| Integrated Process Development Scheme | Eligible projects include: 1) Common effluent treatment plant 2) Captive power generation of technology (preferably renewable/green tech) 3) Infrastructure such as storm water management 4) Facility for testing and R&D veneers The government supports 50% of the total project cost in three installments. |
| Subsidy to Expand Global Markets (International Cooperation Subsidy) | Covers: 1) Reimbursement bases for space rent, airfare, freight charges, advertisement and publicity charges 2) Designed to get representatives from foreign companies into India and representatives from India into foreign companies and governments |
| Energy and Water Conservation | 75% cost of energy / water audit conducted by a recognized institution or consultant 25% of the cost of the equipment recommended by the audit |
Tax Laws:
- Intended for “funding research and innovative projects in clean energy technologies”
- Currently has a coal tax that costs about $6 a ton
- With over 800 million tonnes consumed in 2020, India made roughly $4.8 Billion USD from the tax.
- Problems:
- Poor allocation of the funds
- Only 16% goes to financing climate projects
- Only 32% of fund goes to the National Clean Energy Fund
- Vague definition of acceptable projects: allocated to social problems as well as various subsidies
- High amount of independent finance required
- Private agencies and NGOs must obtain 40% of funds before even applying, and then they can only get 40% of the project to be covered.
- Subsidies to coal industry through tax breaks for mining
- $2.6 Billion USD in 2016
- Poor allocation of the funds
Differences in Climate Investing by State
- Areas in India most inviting to foreign investment:
- Gujarat received the highest FDI equity flows of the US ($21 billion)
- Maharashtra (US $13.64 billion)
- Karnataka (US $6.37 billion)
- Delhi (US $4.22 billion)
- Areas with the most solar power in India:
- Karnataka (7,100 MW)
- Telangana (5,000 MW)
- Rajasthan (4,400 MW)
- Highest potential for solar power.
- Andhra Pradesh (2,470 MW)
- Accounts for 10% of India’s renewables.
- Gujarat (2,654 MW)
- Total renewable energy: 9,670 MW
Opportunities
- India has an incredibly large consumer base and a very educated youth. With 10,000 engineering institutes, India has more engineers than the US and China combined, and 10-12 million young adults are entering the workforce every year.
- This results in a highly competitive workforce
- India is moving towards surpassing the US and China as the largest economy in the world and is expected to become the fastest-growing economy by 2023.
- India attracted the highest ever FDI inflow of $67.54 billion USD in the first 9 months of the 2020-2021 financial year.
Social Stock Exchange
- Securities and Exchange Board of India plans to boost social and environmental impact investing in India.
- Creation of new platform to fund social-sector organizations
- Enable direct listing through a new class of securities
- Establish a standardized framework for measuring and reporting social impact for both donors and investors
Reasons to Consider Investment in India:
- Deep-rooted and highly effective democratic regime, which ensures a calm and stable political environment.
- Well-developed administration and an independent judicial system, along with a vast geography, making the country a repository of resources.
- Workforce is educated, hard-working and skilled (engineers, management staff, accountants and lawyers)
- India hosts an ever-growing consumer base, making it one of the world’s largest markets for manufactured goods and service
- Proximity to key manufacturing sites, key suppliers and low development costs.
- These factors make it an effective base from which multi-national companies can export to other high-growth emerging markets
- Transparency International gave Indian companies the top ranking among emerging market multinationals in terms of transparency and compliance
Click through the regions and points below to learn more about India’s sustainable finance projects.
Chile
- Ranked #1 on BloombergNEF ranking for emerging markets for clean energy investment.
- Chile has exceptional natural resources and the government has set ambitious long-term energy goals.
- By 2024, Chile will phase out 30% of total coal capacity and fully retire coal by 2040.
- Chile has attracted $16 Billion in clean energy investment in the last 7 years.
- As the worlds largest copper exporter, there is a massive energy demand.
- Chile has exceptional natural resources and the government has set ambitious long-term energy goals.